
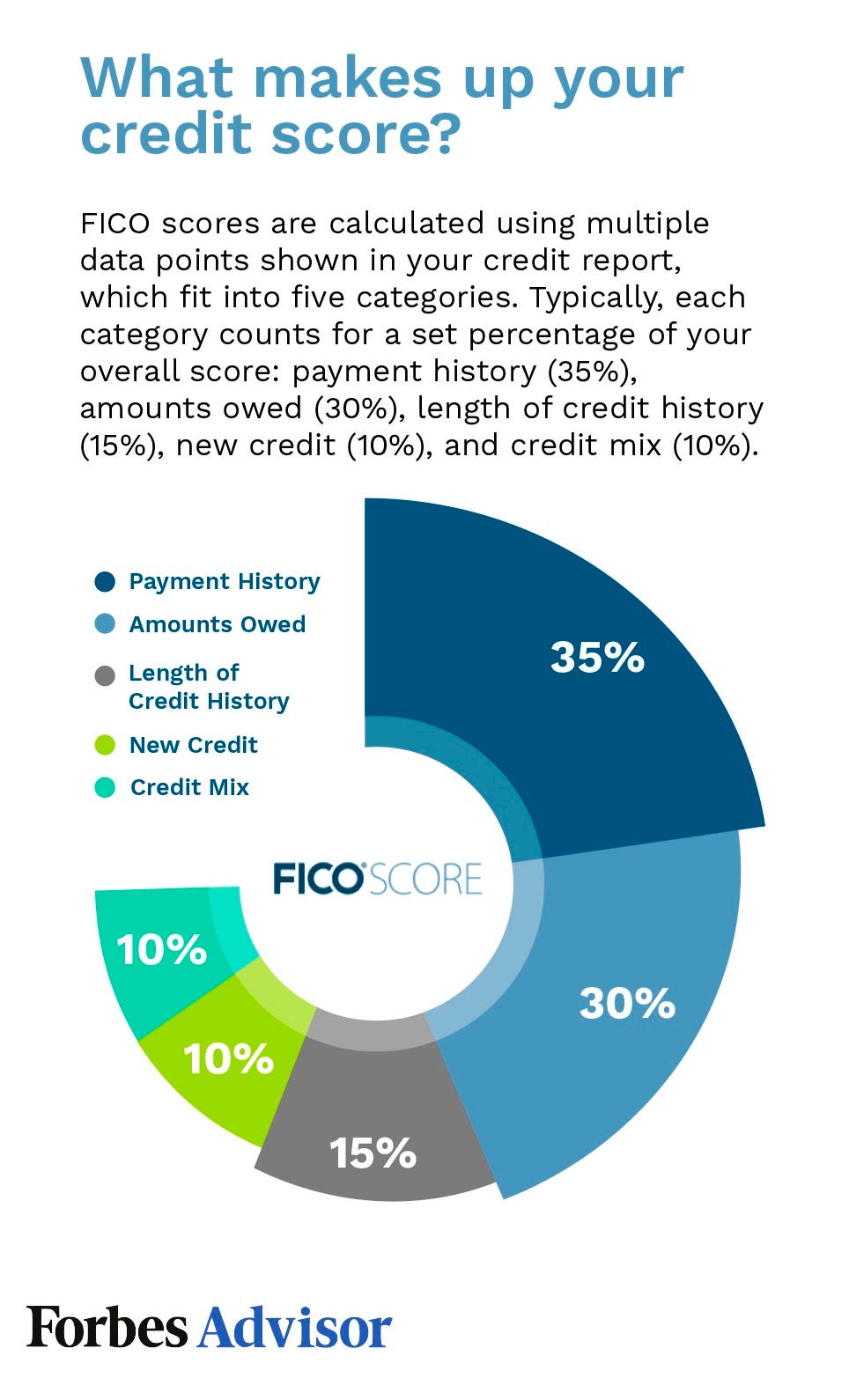
Your credit score is an indicator of your financial position. They will impact your approval for loans and credit cards as well as rent. These factors also impact your interest rates for these loans. Five main factors are used to calculate your credit score. These factors include payment history, credit history, credit length, credit history and new credit.
History of payment
Your credit score is affected by your payment history. Each month, creditors send information about your payments to the major credit bureaus. Late payments can impact your score. Late payments stay on your credit report for seven years. To improve your credit score, ensure that you make your monthly payment on time.
Your credit score is based on your payment history. It displays when you have missed or made late payments. It also gives lenders an idea of how trustworthy you are. Credit bureaus maintain a record of all your payments, as well as the frequency of late payments. You can also view your payment history to learn about bankruptcy, wage attachments or collections.
Age of accounts
Your credit score is affected by the age of your accounts. Lenders consider older customers less risky. This is because their accounts have matured enough to warrant a higher score. However, there are still some factors which can negatively affect an account's ability to age. These factors can vary depending on the scoring model used and the location in which you live.

Calculating the average age for your accounts involves adding all the ages on your credit cards, and then dividing them by how many you have. If you have opened too many new credit cards in a short period of time, the average age will decrease. Generally, the higher the average age, the better.
Payment history ratio
The credit scoring model relies heavily on the Payment history ratio. It looks at a person's payment history and considers how many accounts are delinquent, how often they are late, and any bankruptcy or wage attachment information. High utilization can lead to a decrease in credit scores. To avoid a high utilization rate, it is best to keep your accounts in a low balance.
Credit utilization ratios below 30% can make all the difference to your credit score. High credit utilization is when you use up more credit that you have. High utilization can lead to lower credit scores. Keep track of both your individual ratios as well the overall utilization on all of your credit cards.
Number of accounts on file
Your score will be affected if you have too many accounts. Because lenders want to see information about how prompt you are with your payments, this is a significant factor in determining your score. Your score will decrease the more late payments you make. The other side is that the more accounts you have, the better.
The credit scoring model may take several factors into account, including the types of accounts you have. These include installment loans, and revolving. Multiple accounts are more attractive to lenders because they show that a person can manage multiple types debts. Your credit score could also be affected by how many new accounts you have opened over the past few years.
Scores affected by inquiries
Credit scores inquiries are one the most important parts of your credit report. They can affect your credit score by 0 to 5 points. The impact of an inquiry on your credit score will depend on what type it is and how long ago it has been. It is therefore important to limit the number inquires on your report.
Repeated inquiries on your report will make lenders question your creditworthiness. Multiple inquiries over a short time period will lead to a lower credit score. While multiple inquiries have a negative impact on your credit report, they do not have the same negative impact on your score as several missed repayments or defaults. When calculating your credit score the FICO algorithm will take these inquiries into consideration.